Nanobiotechnology: Applications in Medicine
Nanobiotechnology: Applications in Medicine
Introduction
Nanobiotechnology, the fusion of nanotechnology and biology, is revolutionizing medicine by enabling precise diagnostics, targeted therapies, and innovative treatment approaches. By manipulating biological molecules at the nanoscale, researchers are developing cutting-edge solutions for a wide range of medical challenges, from drug delivery to disease detection.
Key Applications in Medicine
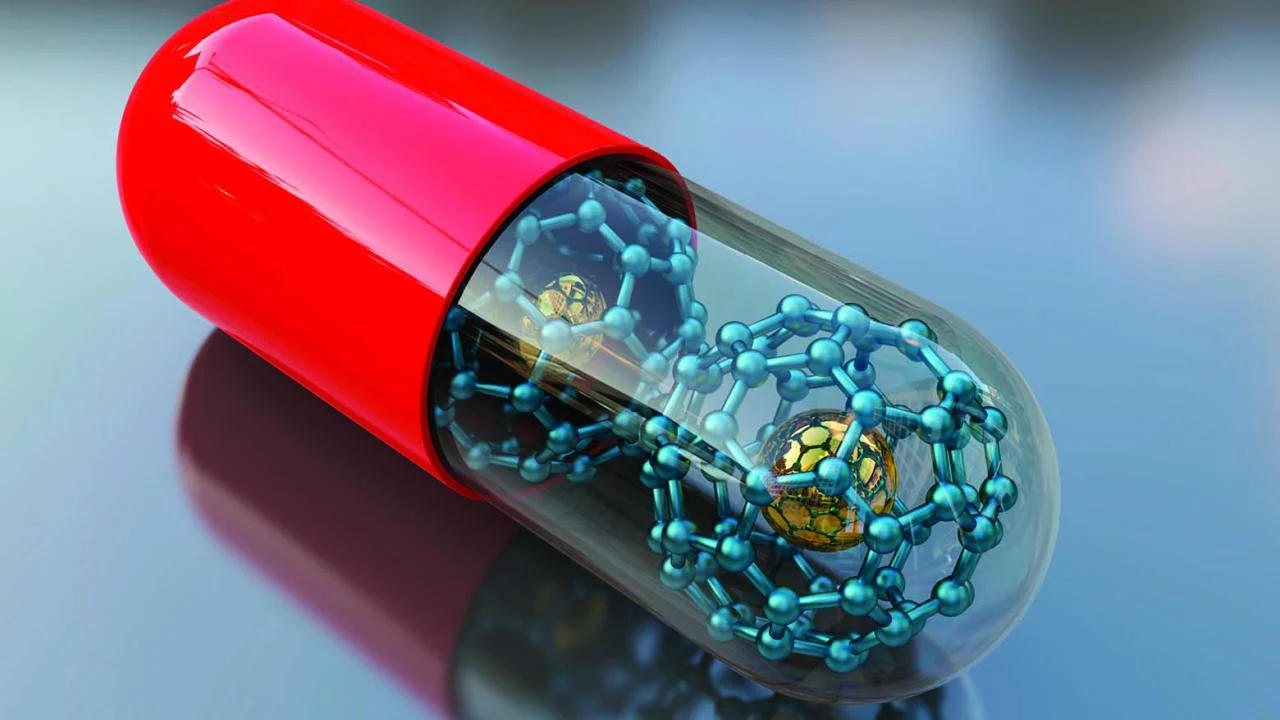
1. Targeted Drug Delivery
Nanoparticles can be engineered to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells, reducing side effects and increasing treatment efficacy. For instance, liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles are used in cancer treatment to ensure chemotherapy drugs reach tumor cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
2. Diagnostics and Imaging
Nanotechnology enhances medical imaging techniques by improving the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tools. Quantum dots and gold nanoparticles are being integrated into biosensors and contrast agents, allowing early detection of diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
3. Regenerative Medicine
Nanomaterials play a crucial role in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Nanoscale scaffolds and hydrogels provide support for cell growth, helping in the regeneration of damaged tissues and organs. Additionally, stem cell therapy is being enhanced with nanotechnology to improve cell differentiation and integration.
4. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Agents
With the rise of antibiotic resistance, nanobiotechnology is offering alternative solutions through antimicrobial nanoparticles. Silver and copper nanoparticles exhibit strong antimicrobial properties, making them useful in wound dressings, coatings for medical devices, and even in treating infections.
5. Gene Therapy and Nanovaccines
Gene therapy is being revolutionized by nanocarriers that can transport genetic material safely into target cells. Additionally, nanovaccines, using nanoparticles to enhance immune responses, are being explored for preventing infectious diseases and even cancer.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its potential, nanobiotechnology faces challenges such as toxicity concerns, regulatory hurdles, and high production costs. Future research aims to address these issues, ensuring the safe and effective integration of nanotechnology into mainstream medicine.
Conclusion
Nanobiotechnology is transforming medicine by providing more efficient, precise, and less invasive treatment options. As research progresses, this field holds the promise of groundbreaking advancements that could redefine healthcare and significantly improve patient outcomes.













